[CCNP] New ENCOR Questions Part 5-2
Question 24
Refer to the exhibit.
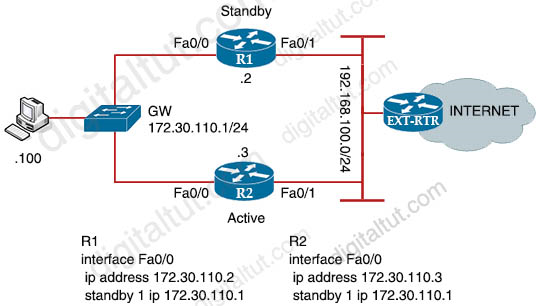
Which configuration change ensures that R1 is the active gateway whenever it is in a functional state for the 172.30.110.0/24 network?
| Option A R1 standby 1 preempt R2 standby 1 priority 90 | Option B R1 standby 1 preempt R2 standby 1 priority 100 |
| Option C R2 standby 1 priority 100 standby 1 preempt | Option D R2 standby 1 priority 110 standby 1 preempt |
A. Option A B. Option B C. Option C D. Option D
Answer: A
Explanation
By default, HSRP does not have preemption enabled so we have to enable it on R1 so that R1 can take the active role of R2. We also need to lower the priority of R2 (to 90) than that of R1 (the default HSRP priority is 100) so that R1 can take the active role.
Question 25
Refer to the exhibit.
| Person#1: First Name is Johnny Last Name is Table Hobbies are: • Running • Video games Person#2 First Name is Billy Last Name is Smith Hobbies are: • Napping • Reading |
Which JSON syntax is derived from this data?
| Option A {‘Person’: [{‘First Name’: ‘Johnny’, ‘Last Name’: ‘Table’, ‘Hobbies’: [‘Running’, ‘Video games’]}, {‘First Name’: ‘Billy’, ‘Last Name’: ‘Smith’, ‘Hobbies’: [‘Napping’, ‘Reading’]}]} | Option B {[{‘First Name’: ‘Johnny’, ‘Last Name’: ‘Table’, ‘Hobbies’: ‘Running’,’Hobbies’: ‘Video games’}, {‘First Name’: ‘Billy’, ‘Last Name’: ‘Smith’, ‘Hobbies’: ‘Napping’, ‘Hobbies’: Reading’}]} |
| Option C {‘Person’: [{‘First Name’:’Johnny’, ‘Last Name’: ‘Table’, ‘Hobbies’: ‘Running’, ‘Video games’}, {‘First Name’: ‘Billy’, ‘Last Name’: ‘Smith’, ‘Hobbies’: ‘Napping’, ‘Reading’}]} | Option D {[{‘First Name’: ‘Johnny’, ‘Last Name’: ‘Table’, ‘Hobbies’: [‘Running’, ‘Video games’]}, {‘First Name’: ‘Billy’, ‘Last Name’: ‘Smith’, ‘Hobbies’: [‘Napping’,’Reading’]}]} |
A. Option A B. Option B C. Option C D. Option D
Answer: A
Explanation
Option B and Option D are not correct because the first square bracket in “{[{” should not be there.
Option C “Hobbies” should be an array, not “‘Hobbies’: ‘Running’, ‘Video games'”
Option A is correct and we also format it in a more comprehensive way below:
{
"Person":[
{
"First Name":"Johnny",
"Last Name":"Table",
"Hobbies":[
"Running",
"Video games"
]
},
{
"First Name":"Billy",
"Last Name":"Smith",
"Hobbies":[
"Napping",
"Reading"
]
}
]
}
Question 26
An engineer creates the configuration below. Drag and drop the authentication methods from the left into the order of priority on the right. Not all options are used.
| R1#sh run | i aaa aaa new-model aaa authentication login default group ACE group AAA_RADIUS local-case aaa session-id common R1# |

Answer:
Step 1: AAA servers of ACE group Step 2: AAA servers of AAA_RADIUS group Step 3: local configured username in case-sensitive format Step 4: If no method works, then deny login
Explanation
The “aaa authentication login default group ACE group AAA_RADIUS local-case” command is broken down as follows:
+ The ‘aaa authentication’ part is simply saying we want to configure authentication settings. + The ‘login’ is stating that we want to prompt for a username/password when a connection is made to the device. + The ‘default’ means we want to apply for all login connections (such as tty, vty, console and aux). If we use this keyword, we don’t need to configure anything else under tty, vty and aux lines. If we don’t use this keyword then we have to specify which line(s) we want to apply the authentication feature. + The ‘group ACE group AAA_RADIUS” means all users are authenticated using group ACE (the first method). If the credentials are not found on this group, then the group AAA_RADIUS is used (the second method). + The ‘local-case‘ option uses case-sensitive local usernames.
Question 27
Refer to the exhibit.

Which two facts does the device output confirm? (Choose two)
A. The device is using the default HSRP hello timer B. The standby device is configured with the default HSRP priority C. The device’s HSRP group uses the virtual IP address 10.0.3.242 D. The device is configured with the default HSRP priority E. The device sends unicast messages to its peers
Answer: A B
Explanation
From the output above, we see the local router is the active HSRP router with priority 110 while the default priority is 100 -> Answer D is not correct.
From the line “Standby router is 10.0.3.242, priority 100”, we learn that standby router is configured with default priority -> Answer B is correct.
HSRP default hello and hold timers are 3 seconds and 10 seconds, respectively so answer A is correct.
Question 28
Based on the output below, which Python code shows the value of the “upTime” key?
| { “response”: [{ “family”: “Routers”, “type”: “Cisco ASR 1001-X Router”, “errorCode”: null, “location”: null, “macAddress”: “00:c8:8b:80:bb:00”, “hostname”: “asr1001-x.abc.inc”, “role”: “BORDER ROUTER”, “lastUpdateTime”: 1577391299537, “serialNumber”: “FXS1932Q1SE”, “softwareVersion”: “16.3.2”, “locationName”: null, “upTime”: “49 days, 13:43:44:13”, “lastUpdated”: “2019-12-22 16:35:21” }] } |
| Option A json_data = response.json() print(json_data[response][0][upTime]) | Option B json_data = response_json() print(json_data[‘response’][‘family’][‘upTime’]) |
| Option C json_data = response.json() print(json_data[‘response’][0][‘upTime’]) | Option D json_data = json.loads(response.text) print(json_data[‘response’][‘family’][‘upTime’]) |
A. Option A B. Option B C. Option C D. Option D
Answer: C
Explanation
You can test this question in Python and see the output below:

Note: We need to call the first element “[0]” in “json_data[‘response’][0][‘upTime’])” command because “response” is an array with only one element.
Question 29
Which two actions, when applied in the LAN network segment, will facilitate Layer 3 CAPWAP discovery for lightweight AP? (Choose two)
A. Utilize DHCP option 17 B. Utilize DHCP option 43 C. Configure WLC IP address on LAN switch D. Enable port security on the switch port E. Configure an ip helper-address on the router interface
Answer: B E
Explanation
In a Cisco Unified Wireless network, the LAPs must first discover and join a WLC before they can service wireless clients. However, this presents a question: how did the LAPs find the management IP address of the controller when it is on a different subnet? If you do not tell the LAP where the controller is via DHCP option 43, DNS resolution of “Cisco-capwap-controller.local_domain”, or statically configure it, the LAP does not know where in the network to find the management interface of the controller.
Question 30
Refer to the exhibit.
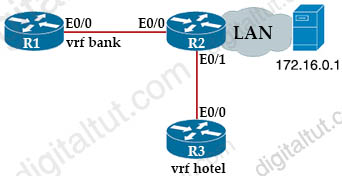
R2:
vrf definition hotel
address-family ipv4
exit-address-family
vrf definition bank
address-family ipv4
exit-address-family
interface Ethernet0/0
vrf forwarding bank
ip address 172.16.0.4 255.255.0.0
interface Ethernet0/1
vrf forwarding hotel
ip address 172.1.0.5 255.255.0.0
router ospf 42 vrf bank
router-id 1.1.1.1
network 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 0
router ospf 43 vrf hotel
router-id 3.3.3.3
network 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 0
R1:
vrf definition bank
!
address-family ipv4
exit-address-family
Which configuration must be applied to R1 to enable R1 to reach the server at 172.16.0.1?
| Option A interface Ethernet0/0 ip address 172.16.0.7 255.255.0.0 ! router ospf 44 vrf hotel network 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 | Option B interface Ethernet0/0 vrf forwarding bank ip address 172.16.0.7 255.255.0.0 ! router ospf 44 vrf bank network 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 0 |
| Option C interface Ethernet0/0 vrf forwarding hotel ip address 172.16.0.7 255.255.0.0 ! router ospf 44 vrf hotel network 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 0 | Option D interface Ethernet0/0 ip address 172.16.0.7 255.255.0.0 ! router ospf 44 vrf bank network 172.16.0.0 255.255.0.0 |
A. Option A B. Option B C. Option C D. Option D
Answer: B
Question 31
The following system log message is presented after a network administrator configures a GRE tunnel:
| %TUN-RECURDOWN: Interface Tunnel 0 temporarily disabled due to recursive routing. |
Why is Tunnel 0 disabled?
A. Because the tunnel cannot reach its tunnel destination B. Because the best path to the tunnel destination is through the tunnel itself C. Because dynamic routing is not enabled D. Because the router cannot recursively identify its egress forwarding interface
Answer: B
Explanation
The %TUN-5-RECURDOWN: Tunnel0 temporarily disabled due to recursive routing error message means that the generic routing encapsulation (GRE) tunnel router has discovered a recursive routing problem. This condition is usually due to one of these causes: + A misconfiguration that causes the router to try to route to the tunnel destination address using the tunnel interface itself (recursive routing) + A temporary instability caused by route flapping elsewhere in the network
======================= New Questions (added on 9th-Mar-2020) =======================
Question 32
What is provided by the Stealthwatch component of the Cisco Cyber Threat Defense solution?
A. real-time threat management to stop DDoS attacks to the core and access networks B. real-time awareness of users, devices and traffic on the network C. malware control D. dynamic threat control for web traffic
Answer: B
Explanation
Cisco Stealthwatch is a comprehensive, network telemetry-based, security monitoring and analytics solution that streamlines incident response through behavioral analysis; detecting denial of service attacks, anomalous behaviour, malicious activity and insider threats. Based on a scalable enterprise architecture, Stealthwatch provides near real-time situational awareness of all users and devices on the network.
Reference: https://www.endace.com/cisco-stealthwatch-solution-brief.pdf
Note: Although answer A seems to be correct but in fact, Stealthwatch does not provide real-time protection for DDoS attack. It just helps detect DDoS attack only.
Stealthwatch aggregates observed network activity and performs behavioral and policy driven analytics against what it sees in order to surface problematic activities. While we don’t position our self as a DDOS solution, we’re going to leverage our analytical capabilities to identify a DDoS attack against an internal host using the WebUI.
Reference: https://www.ciscolive.com/c/dam/r/ciscolive/us/docs/2016/pdf/LTRSEC-8421-LG.pdf
Question 33
How does Protocol Independent Multicast function?
A. It uses unicast routing information to perform the multicast forwarding function. B. It uses the multicast routing table to perform the multicast forwarding function. C. In sparse mode it establishes neighbor adjacencies and sends hello messages at 5-second intervals. D. It uses broadcast routing information to perform the multicast forwarding function.
Answer: A
Explanation
Although PIM is called a multicast routing protocol, it actually uses the unicast routing table to perform the reverse path forwarding (RPF) check function instead of building up a completely independent multicast routing table. Unlike other routing protocols, PIM does not send and receive routing updates between routers.
Question 34
Under which network conditions is an outbound QoS policy that is applied on a router WAN interface most beneficial?
A. under all network conditions B. under network convergence conditions C. under interface saturation conditions D. under traffic classification and marking conditions
Answer: C
Question 35
Which technology does VXLAN use to provide segmentation for Layer 2 and Layer 3 traffic?
A. bridge domain B. VLAN C. VRF D. VNI
Answer: D
Explanation
VXLAN has a 24-bit VXLAN network identifier (VNI), which allows for up to 16 million (= 224) VXLAN segments to coexist within the same infrastructure. This surely solve the small number of traditional VLANs.
Question 36
A company has an existing Cisco 5520 HA cluster using SSO. An engineer deploys a new single Cisco Catalyst 9800 WLC to test new features. The engineer successfully configures a mobility tunnel between the 5520 cluster and 9800 WLC. Clients connected to the corporate WLAN roam seamlessly between access points on the 5520 and 9800 WLC. After a failure on the primary 5520 WLC, all WLAN services remain functional; however clients cannot roam between the 5520 and 9800 controllers without dropping their connection. Which feature must be configured to remedy the issue?
A. mobility MAC on the 5520 cluster B. mobility MAC on the 9800 WLC C. new mobility on the 5520 cluster D. new mobility on the 9800 WLC
Answer: B
Question 37
What are two methods of ensuring that the multicast RPF check passes without changing the unicast routing table? (Choose two)
A. disabling BGP routing protocol B. implementing static mroutes C. disabling the interface of the router back to the multicast source D. implementing MBGP E. implementing OSPF routing protocol
Answer: B D
Question 38
What is the result when an active route processor fails in a design that combines NSF with SSO?
A. An NSF-aware device immediately updates the standby route processor RIB without churning the network B. The standby route processor temporarily forwards packets until route convergence is complete C. An NSF-capable device immediately updates the standby route processor RIB without churning the network D. The standby route processor immediately takes control and forwards packets along known routes
Answer: B
=========================== New Questions (added on 28th-Mar-2021) ===========================
Question 39
What is a benefit of a virtual machine when compared with a physical server?
A. Deploying a virtual machine is technically less complex than deploying a physical server. B. Virtual machines increase server processing performance. C. The CPU and RAM resources on a virtual machine cannot be affected by other virtual machines. D. Multiple virtual servers can be deployed on the same physical server without having to buy additional hardware.
Answer: D
Question 40
What is the wireless received signal strength indicator?
A. The value of how strong the wireless signal is leaving the antenna using transmit power, cable loss, and antenna gain B. The value given to the strength of the wireless signal received compared to the noise level C. The value of how much wireless signal is lost over a defined amount of distance D. The value of how strong a wireless signal is received, measured in dBm
Answer: D
Explanation
RSSI, or “Received Signal Strength Indicator,” is a measurement of how well your device can hear a signal from an access point or router. It’s a value that is useful for determining if you have enough signal to get a good wireless connection.
This value is measured in decibels (dBm) from 0 (zero) to -120 (minus 120). The closer to 0 (zero) the stronger the signal is which means it’s better, typically voice networks require a -65db or better signal level while a data network needs -80db or better.
Question 41
Which controller is capable of acting as a STUN server during the onboarding process of Edge devices?
A. vManage B. vSmart C. vBond D. PNP server
Answer: C
Explanation
An additional vBond is deployed on the Internet and acts as a STUN server for WAN Edge devices with Internet access and redirects them to the private controller IP addresses.
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/solutions/CVD/SDWAN/cisco-sdwan-design-guide.html
Note: Session Traversal Utilities for NAT (STUN) is a standardized set of methods, including a network protocol, for traversal of network address translator (NAT) gateways in applications of real-time voice, video, messaging, and other interactive communications.
Question 42
What is the process for moving a virtual machine from one host machine to another with no downtime?
A. live migration B. disaster recovery C. high availability D. multisite replication
Answer: A
Explanation
Live migration refers to the process of moving a running virtual machine or application between different physical machines without disconnecting the client or application. Memory, storage, and network connectivity of the virtual machine are transferred from the original guest machine to the destination. An example of live migration tool is VMware vSphere vMotion.
Question 43
What are two features of NetFlow flow monitoring? (Choose two)
A. Can track ingress and egress information B. Include the flow record and the flow importer C. Copies all ingress flow information to an interface D. Does not required packet sampling on interfaces E. Can be used to track multicast, MPLS, or bridged traffic
Answer: A E
Explanation
The following are restrictions for Flexible NetFlow: + Traditional NetFlow (TNF) accounting is not supported. + Flexible NetFlow v5 export format is not supported, only NetFlow v9 export format is supported. + Both ingress and egress NetFlow accounting is supported. + Microflow policing feature shares the NetFlow hardware resource with FNF. + Only one flow monitor per interface and per direction is supported.
When configuring NetFlow, follow these guidelines and restrictions:
+ Except in PFC3A mode, NetFlow supports bridged IP traffic. PFC3A mode does not support NetFlow bridged IP traffic. + NetFlow supports multicast IP traffic.
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/general/Test/dwerblo/broken_guide/netflow.html
The Flexible NetFlow – MPLS Egress NetFlow feature allows you to capture IP flow information for packets that arrive on a router as Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) packets and are transmitted as IP packets. This feature allows you to capture the MPLS VPN IP flows that are traveling through the service provider backbone from one site of a VPN to another site of the same VPN
Question 44
Which method should an engineer use to deal with a long-standing contention issue between any two VMs on the same host?
A. Adjust the resource reservation limits B. Reset the host C. Reset the VM D. Live migrate the VM to another host
Answer: A
Question 45
What is the recommended MTU size for a Cisco SD-Access Fabric?
A. 4464 B. 9100 C. 1500 D. 17914
Answer: B
Question 46
What does the number in an NTP stratum level represent?
A. The number of hops it takes to reach the master time server. B. The amount of drift between the device clock and true time. C. The amount of offset between the device clock and true time. D. The number of hops it takes to reach the authoritative time source.
Answer: D
Explanation
NTP uses the concept of a stratum to describe how many hops (routers) away a machine is from an authoritative time source, usually a reference clock. A reference clock is a stratum 0 device that is assumed to be accurate and has little or no delay associated with it. Stratum 0 servers cannot be used on the network but they are directly connected to computers which then operate as stratum-1 servers. A stratum 1 time server acts as a primary network time standard.

Question 47
Refer to the exhibit.

| R1(config)#ip sla 1 R1(config-ip-sla)#icmp-echo 172.20.20.2 source-interface FastEthernet1/0 R1(config-ip-sla-echo)#timeout 5000 R1(config-ip-sla-echo)#frequency 10 R1(config-ip-sla-echo)#threshold 500 R1(config)#ip sla schedule 1 start-time now life forever R1(config)#track 10 ip sla 1 reachability R1(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.20.20.2 |
After implementing the configuration 172.20.20.2 stops replaying to ICMP echoes, but the default route fails to be removed. What is the reason for this behavior?
A. The source-interface is configured incorrectly. B. The destination must be 172.30.30.2 for icmp-echo C. The default route is missing the track feature D. The threshold value is wrong
Answer: C
Explanation
The last command should be “R1(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.20.20.2 track 10”.
Question 48
Refer to the exhibit.
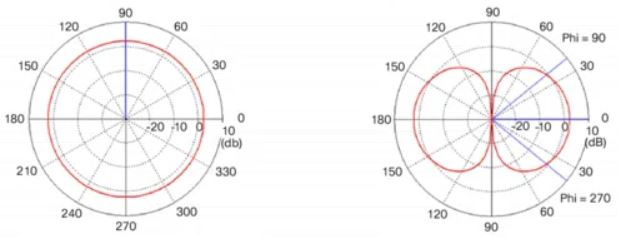
Which type of antenna is show on the radiation patterns?
A. Dipole B. Yagi C. Patch D. Omnidirectional
Answer: A
Explanation
A dipole antenna most commonly refers to a half-wavelength (λ/2) dipole. The physical antenna (not the package that it is in) is constructed of conductive elements whose combined length is about half of a wavelength at its intended frequency of operation. This is a simple antenna that radiates its energy out toward the horizon (perpendicular to the antenna). The patterns shown are those resulting from a perfect dipole formed with two thin wires oriented vertically along the z-axis.
Question 49
Drag and drop characteristics of PIM dense mode from the left to the right.
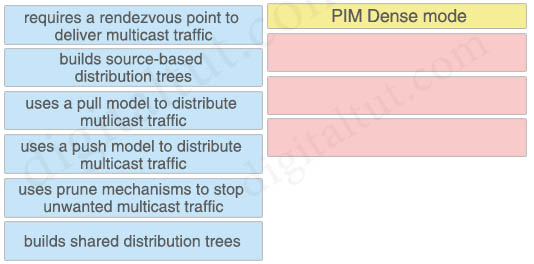
Answer:
PIM Dense Mode: + builds source-based distribution trees + uses a push model to distribute multicast traffic + uses prune mechanisms to stop unwanted multicast traffic
Explanation
PIM-DM supports only source trees – that is, (S,G) entries–and cannot be used to build a shared distribution tree.
PIM dense mode (PIM-DM) uses a push model to flood multicast traffic to every corner of the network. This push model is a brute-force method of delivering data to the receivers. This method would be efficient in certain deployments in which there are active receivers on every subnet in the network. PIM-DM initially floods multicast traffic throughout the network. Routers that have no downstream neighbors prune the unwanted traffic. This process repeats every 3 minutes.
A rendezvous point (RP) is required only in networks running Protocol Independent Multicast sparse mode (PIM-SM).
In PIM dense mode (PIM-DM), multicast traffic is initially flooded to all segments of the network. Routers that have no downstream neighbors or directly connected receivers prune back the unwanted traffic.
Question 50
Refer to the exhibit
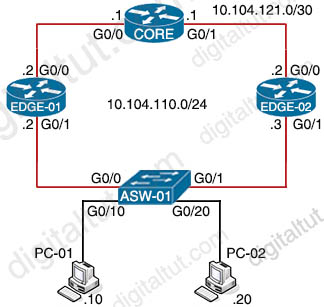
| Edge-01 track 10 interface GigabitEthernet0/0 line-protocol ! interface GigabitEthernet0/1 ip address 10.104.110.2 255.255.255.0 vrrp 10 ip 10.104.110.100 vrrp 10 priority 120 |
Edge-02 interface GigabitEthernet0/1 ip address 10.104.110.3 255.255.255.0 vrrp 10 ip 10.104.110.100 |
Object tracking has been configured for VRRP enabled routers Edge-01 and Edge-02. Which commands cause Edge-02 to preempt Edge-01 in the event that interface G0/0 goes down on Edge-01?
| Option A Edge-01(config)#interface G0/1 Edge-01(config-if)#vrrp 10 track 10 decrement 10 |
Option B Edge-02(config)#interface G0/1 Edge-02(config-if)#vrrp 10 track 10 decrement 30 |
| Option C Edge-02(config)#interface G0/1 Edge-02(config-if)#vrrp 10 track 10 decrement 10 |
Option D Edge-01(config)#interface G0/1 Edge-01(config-if)#vrrp 10 track 10 decrement 30 |
A. Option A B. Option B C. Option C D. Option D
Answer: D
Question 51
Which protocol is implemented to establish secure control plane adjacencies between Cisco SD-WAN nodes?
A. IKE B. DTLS C. IPsec D. ESP
Answer: B
Explanation
The Cisco SD-WAN control plane has been designed with network and device security in mind. The foundation of the control plane is one of two security protocols derived from SSL (Secure Sockets Layer)—the Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS) protocol and the Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol.

Question 52
Refer to the exhibit.
flow monitor FLOW-MONITOR-1
record netflow ipv6 original-input
exit
!
sampler SAMPLER-1
mode deterministic 1 out-of 2
exit
!
ip cef
ipv6 cef
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0
ipv6 address 2001:DB8:2:ABCD::2/48
ipv6 flow monitor FLOW-MONITOR-1 sampler SAMPLER-1 input
What is the effect of introducing the sampler feature into the Flexible NetFlow configuration on the router?
A. NetFlow updates to the collector are sent 50% less frequently. B. Every second IPv4 packet is forwarded to the collector for inspection. C. CPU and memory utilization are reduced when compared with what is required for full NetFlow. D. The resolution of sampling data increases, but it requires more performance from the router.
Answer: A
Explanation
The example above shows how to configure and enable deterministic sampling for IPv6 input traffic -> Answer B is not correct.
Answer D is not correct because “1 out-of 2” mode will only sample 1 out of 2 packets, thus the resolution of sampling data will decrease (not increase)
There is three sampling modes: – deterministic: select each N-th observed flow – random: select randomly one out of N flows. – hash: select hash-randomly one out of N flows.
Using ‘deterministic’ and ‘random’ sampling will not reduce resource usage caused by the module, because flows are sampled late in exporting process. This will reduces amount of flows which go to the collector, thus, reducing load on the collector -> Answer A is correct.
Reference: https://github.com/aabc/pkt-netflow
CPU is not involved in the process of packet sampling as it is done by the hardware (ASICs) -> Answer C is not correct.
Question 53
When does a stack master lose its role?
A. When the priority value of a stack member is changed to a higher value B. When a switch with a higher priority is added to the stack C. When the stack master is reset D. When a stack member fails
Answer: C
Explanation
A stack master retains its role unless one of these events occurs: + The switch stack is reset.* + The stack master is removed from the switch stack. + The stack master is reset or powered off -> Answer C is correct. + The stack master fails. + The switch stack membership is increased by adding powered-on standalone switches or switch stacks.*
In the events marked by an asterisk (*), the current stack master might be reelected based on the listed factors.
Question 54
What is the calculation that is used to measure the radiated power of a signal after it has gone through the radio, antenna cable, and antenna?
A. dBi B. mW C. dBm D. EIRP
Answer: D
Explanation
Once you know the complete combination of transmitter power level, the length of cable, and the antenna gain, you can figure out the actual power level that will be radiated from the antenna. This is known as the effective isotropic radiated power (EIRP), measured in dBm.
EIRP is a very important parameter because it is regulated by governmental agencies in most countries. In those cases, a system cannot radiate signals higher than a maximum allowable EIRP. To find the EIRP of a system, simply add the transmitter power level to the antenna gain and subtract the cable loss.

EIRP = Tx Power – Tx Cable + Tx Antenna
Suppose a transmitter is configured for a power level of 10 dBm (10 mW). A cable with 5-dB loss connects the transmitter to an antenna with an 8-dBi gain. The resulting EIRP of the system is 10 dBm – 5 dB + 8 dBi, or 13 dBm.
You might notice that the EIRP is made up of decibel-milliwatt (dBm), dB relative to an isotropic antenna (dBi), and decibel (dB) values. Even though the units appear to be different, you can safely combine them because they are all in the dB “domain”.
Reference: CCNA Wireless 640-722 Official Cert Guide