New ENCOR Questions – Part 5
Question 1
Drag and drop the solutions that comprise Cisco Cyber Threat Defense from the left onto the objectives they accomplish on the right.

Answer:
+ detects suspicious web activity: Web Security Appliance + analyzes network behavior and detects anomalies: StealthWatch + uses pxGrid to remediate security threats: Identity Services Engine
Explanation
Cisco ISE collects dynamic contextual data from throughout the network and uses Cisco pxGrid technology, a robust context-sharing platform, to share that deeper level of contextual data about connected users and devices with external and internal ecosystem partner solutions. Through the use of a single API, Cisco ISE network and security partners use this data in order to improve their own network access capabilities and accelerate their solutions’ capabilities to identify, mitigate, and remediate network threats.
StealWatch: performs security analytics by collecting network flows via NetFlow
Question 2
What are two characteristics of Cisco SD-Access elements? (Choose two)
A. Fabric endpoints are connected directly to the border node B. The border node is required for communication between fabric and nonfabric devices C. The control plane node has the full RLOC-to-EID mapping database D. Traffic within the fabric always goes through the control plane node E. The border node has the full RLOC-to-EID mapping database
Answer: B C
Explanation
There are five basic device roles in the fabric overlay: + Control plane node: This node contains the settings, protocols, and mapping tables to provide the endpoint-to-location (EID-to-RLOC) mapping system for the fabric overlay. + Fabric border node: This fabric device (for example, core layer device) connects external Layer 3 networks to the SDA fabric. + Fabric edge node: This fabric device (for example, access or distribution layer device) connects wired endpoints to the SDA fabric. + Fabric WLAN controller (WLC): This fabric device connects APs and wireless endpoints to the SDA fabric. + Intermediate nodes: These are intermediate routers or extended switches that do not provide any sort of SD-Access fabric role other than underlay services.
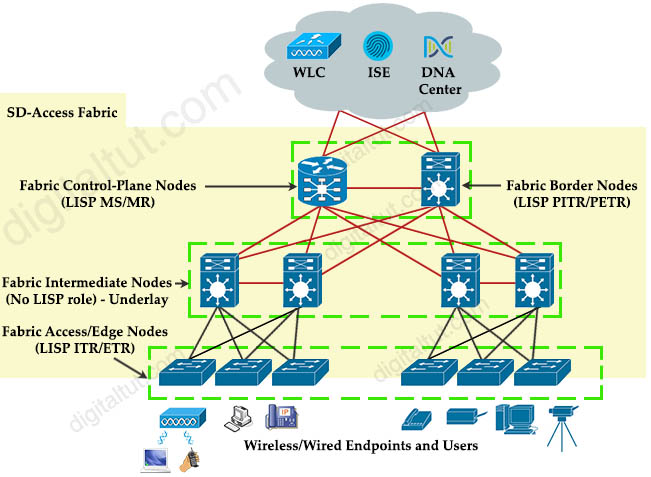
Reference: CCNP and CCIE Enterprise Core ENCOR 350-401 Official Cert Guide
Question 3
Refer to the exhibit.
Current configuration: 142 bytes
vrf definition STAFF
!
!
interface GigabitEthernet1
vrf forwarding STAFF
no ip address
negotiation auto
no mop enabled
no mop sysid
end
An engineer must assign an IP address of 192.168.1.1/24 to the GigabitEthemet1 interface. Which two commands must be added to the existing configuration to accomplish this task? (Choose two)
A. Router(config-vrf)#address-family ipv6 B. Router(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 C. Router(config-vrf)#ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 D. Router(config-if)#address-family ipv4 E. Router(config-vrf)#address-family ipv4
Answer: B E
Explanation
In fact we only need to assign IP address to Gi1 with the command “Router(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0”. The command “Router(config-vrf)#address-family ipv4” is unnecessary unless we have other configurations.
Question 4
What is the data policy in a Cisco SD-WAN deployment?
A. list of ordered statements that define node configurations and authentication used within the SD-WAN overlay B. Set of statements that defines how data is forwarded based on IP packet information and specific VPNs C. detailed database mapping several kinds of addresses with their corresponding location D. group of services tested to guarantee devices and links liveliness within the SD-WAN overlay
Answer: B
Explanation
Data policy operates on the data plane in the Cisco SD-WAN overlay network and affects how data traffic is sent among Cisco SD-WAN devices in the network. The Cisco SD-WAN architecture defines two types of data policy, centralized data policy, which controls the flow of data traffic based on the IP header fields in the data packets and based on network segmentation, and localized data policy, which controls the flow of data traffic into and out of interfaces and interface queues on the devices.
Question 5
Refer to the exhibit.

Which action resolves the EtherChannel issue between SW2 and SW3?
A. Configure switchport mode trunk on SW2 B. Configure switchport nonegotiate on SW3 C. Configure channel-group 1 mode desirable on both interfaces D. Configure channel-group 5 mode active on both interfaces
Answer: C
Explanation
From the output we learn that SW2 is running PAgP while Sw3 is running LACP so they cannot form Etherchannel. Therefore we need to configure only LACP (active mode) or PAgP (desirable mode) on both switches. But we have to configure on the existing “channel-group 1”, not group 5.
Question 6
Refer to the exhibit.

A network engineer configures OSPF and reviews the router configuration. Which interface or interfaces are able to establish OSPF adjacency?
A. GigabitEthemet0/1 and GigabitEthernet0/1.40 B. Gigabit Ethernet0/0 and GigabitEthemet0/1 C. only GigabitEthernet0/0 D. only GigabitEthernet0/1
Answer: C
Explanation
This is the output of command “show ip ospf interface”. From the line “No hellos (Passive interface)”, we learn that interface Gi0/1 was configured passive interface -> It cannot establish OSPF adjacency. Only Gi0/0 established OSPF adjacency.
Note: DROTHER is just a sign of FULL state in OSPF but this router is not a DR or BDR. Therefore DROTHER means interface was established adjacency successfully with the neighbor interface.
Question 7
Refer to the exhibit
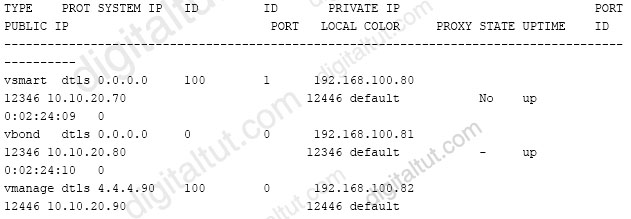

What step resolves the authentication issue?
A. restart the vsmart host B. target 192.168.100.82 in the URI C. change the port to 12446 D. use basic authentication
Answer: B
Explanation
The first figure is the output of the “show control connections” command. From this figure we learned that the vManage IP address is 192.168.100.82 so we need to connect to this IP address (not 192.168.100.80).
Question 8
Refer to the exhibit

A network engineer must simplify the IPsec configuration by enabling IPsec over GRE using IPsec profiles. Which two configuration changes accomplish this? (Choose two)
A. Apply the crypto map to the tunnel interface and change the tunnel mode to tunnel mode ipsec ipv4 B. Remove all configuration related to crypto map from R1 and R2 and eliminate the ACL 100 C. Remove the crypto map and modify the ACL to allow traffic between 10.10.0.0/24 to 10.20.0.0/24 D. Create an IPsec profile, associate the transform-set, and apply the profile to the tunnel interface
Answer: B D
Explanation
In this question, we have to grasp the difference between the old configuration of GRE over IPSec with crypto map versus the new configuration of Tunnel Protection (or IPsec Profile).
In the old method, an extended ACL must be defined to match which traffic will be encrypted, since we configure GRE as the encapsulation protocol for all IP packet, traditionally we used an ACL (100, in our case) to match the GRE packet sourced from 209.165.201.1 and destined to 209.165.201.6 because all traffic that goes through the tunnel will encapsulated with the Public IP header defined in the tunnel source and tunnel destination command under the tunnel interface.
Then after setting this ACL, we need the crypto map for phase 2 IPsec. Under the crypto map, we put in the peer address, transform-set and the above ACL. Finally we apply the crypto map on the physical interface. There are many duplicated configuration in this old method! For example, we need to define the same source and destination addresses in the ACL and the interface tunnel. Or use the same destination address in “set peer” command under crypto map and “tunnel destination” command under interface tunnel.
In the new IPSec Profile configuration, we only need to create an IPsec Profile, associate the transform-set and apply the IPsec Profile on the Tunnel interface and that’s all! There are is no need of ACL or crypto map. All the information (including source and destination IP addresses) are already there in the tunnel interface.
An example of configuring IPSec over GRE Tunnel with IPSec Profile is shown below:
| crypto isakmp policy 2 encrypt aes 256 authentication pre-share group 2 ! crypto isakmp key ****** address 200.16.1.5 ! crypto ipsec transform-set ESP-AES-256-SHA esp-aes 256 esp-sha-hmac ! crypto ipsec profile VTI set transform-set ESP-AES-256-SHA set pfs group2 ! interface tunnel 1 ip address 2.2.2.1 255.255.255.254 tunnel mode ipsec ipv4 tunnel destination 200.16.1.5 tunnel protection ipsec profile VTI |
Reference: https://ipdemystify.com/2020/11/16/ipsec-crypto-map-vs-tunnel-protection-demystified/
Question 9
Which encryption hashing algorithm does NTP use for authentication?
A. SSL B. AES256 C. AES128 D. MD5
Answer: D
Explanation
An example of configuring NTP authentication is shown below:
Router1(config)#ntp authentication-key 2 md5 9tut Router1(config)#ntp authenticate Router1(config)#ntp trusted-key 2
Question 10
What is a VPN in a Cisco SD-WAN deployment?
A. virtual channel used to carry control plane information B. attribute to identify a set of services offered in specific places in the SD-WAN fabric C. common exchange point between two different services D. virtualized environment that provides traffic isolation and segmentation in the SD-WAN fabric
Answer: D
Question 11
Drag and drop the characteristic from the left onto the orchestration tools that they describe on the right.

Answer:
Ansible: + uses playbooks + prodedural
Puppet: + uses a pull model + declarative
Explanation
In Ansible, Playbooks are files that provide actions and logic about what Ansible should do. Ansible playbooks are files that contain tasks to configure hosts. Ansible playbooks are written in YAML format.
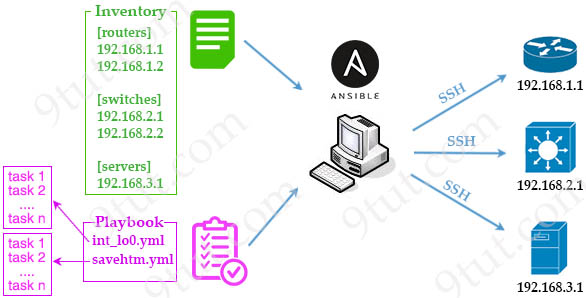
Puppet is based on a Pull deployment model, where the nodes check in regularly after every 1800 seconds with the Master to see if anything needs to be updated in the agent. If anything needs to be updated the agent pulls the necessary Puppet codes from the Master and performs required actions.

Chef and Ansible encourage a procedural style where you write code that specifies, step-by-step, how to to achieve some desired end state. Terraform, SaltStack, and Puppet all encourage a more declarative style where you write code that specifies your desired end state, and the IAC tool itself is responsible for figuring out how to achieve that state.
Question 12
Refer to the exhibit.

Communication between London and New York is down. Which command set must be applied to resolve this issue?
| Option A NewYork(config)#int f0/1 NewYork(config)#switchport nonegotiate NewYork(config)#end NewYork# | Option B NewYork(config)#int f0/1 NewYork(config)#switchport trunk encap dot1q NewYork(config)#end NewYork# |
| Option C NewYork(config)#int f0/1 NewYork(config)#switchport mode dynamic desirable NewYork(config)#end NewYork# | Option D NewYork(config)#int f0/1 NewYork(config)#switchport mode trunk NewYork(config)#end NewYork# |
A. Option A B. Option B C. Option C D. Option D
Answer: B
Explanation
From the output line “TOT/TAT/TNT: NATIVE/ISL/NATIVE”, we see interface f0/1 of NewYork router is hard coded ISL which is mismatched with 802.1Q so we have to change trunking encapsulation on NewYork router to 802.1Q.
Note: The TOS/TAS/TNS of “ACCESS/AUTO/ACCESS” shows it is currently operating as an Access Port, in Dynamic Auto mode, and its negotiated to be an Access Port (but it can be negotiated to become a trunk port).
Note:
TOS = Trunk Operational Status TAS = Trunk Administrative Status TNS = Trunk Negotiation Status TOT = Trunk Operational Type TAT = Trunk Administrative Type TNT = Trunk Negotiation Type
Question 13
What is an emulated machine that has dedicated compute, memory, and storage resources and a fully installed operating system?
A. host B. virtual machine C. container D. mainframe
Answer: B
Question 14
Which two methods are used to reduce the AP coverage area? (Choose two)
A. Reduce AP transmit power B. Increase minimum mandatory data rate C. Reduce channel width from 40 MHz to 20 MHz D. Enable Fastlane E. Disable 2.4 GHz and use only 5 GHz
Answer: A B
Explanation
The transmit power of an AP affects the wireless coverage area and the maximum achievable signal-to-noise ratio. Proper configuration of transmit power is important for ensuring a wireless network is operating at its highest capacity.
Reference: https://documentation.meraki.com/MR/Radio_Settings/Transmit_Power_and_Antenna_Configuration
AP coverage area or the cell size, according to this Cisco link, there are two ways to reduce the AP coverage area: + Tuning Cell Size with Transmit Power + Tuning Cell Size with Data Rates
Setting the transmit power level is a simplistic approach to defining the cell size, but that is not the only variable involved. The cell size of an AP is actually a compromise between its transmit power and the data rates that it offers.
To design a wireless LAN for best performance, you would most likely need to disable some of the lower data rates. For example, you could disable the 1, 2, and 5.5 Mbps rates to force clients to use higher rates and better modulation and coding schemes. That would improve throughput for individual clients and would also benefit the BSS as a whole by eliminating the slower rates that use more time on a channel.

-> Therefore increasing minimum mandatory data rate would reduce coverage area but enhance performance.
Question 15
Which data is properly formatted with JSON
B. Option B C. Option C D. Option D
Answer: D
Explanation
Option A is missing commas. Option B is missing one comma behind “age”:25 and the trailing comma needs to be removed. Option C needs to remove the trailing comma.
Question 16
Drag and drop the descriptions of the VSS technology from the left to the right. Not all options are used.

Answer:
VSS: + supported on the Cisco 4500 and 6500 series + combines exactly two devices + supports devices that are geographically separated
Explanation
The following characteristics are correct for StackWise (but not VSS): + can be connected in up to 9 devices + is supported only on line 3750 and (2960/3650/3850/3750+) + uses proprietary cable for connection
Question 17
Refer to the exhibit.

All switches are configured with the default port priority value. Which two commands ensure that traffic from PC1 is forwarded over Gi1/3 trunk port between DWS1 and DSW2? (Choose two)
A. DWS1(config-if)#spanning-tree port-priority 0 B. DSW2(config-if)#spanning-tree port-priority 16 C. DSW1(config-if)#interface gi1/3 D. DSW2(config-if)#interface gi1/3 E. DSW2(config-if)#spanning-tree port-priority 128
Answer: B D
Explanation
In this topology, DSW2 is the root bridge because of lowest Bridge Priority (24576) so all of its ports are in forwarding state. DSW1 needs to block one of its ports to DSW2 to avoid a bridging loop between the two switches. Unfortunately, DSW blocked port Gi1/3. But how does DSW1 select its blocked port? Well, the answer is based on the BPDUs it receives from DSW2. A BPDU is superior than another if it has: 1. A lower Root Bridge ID 2. A lower path cost to the Root 3. A lower Sending Bridge ID 4. A lower Sending Port ID
These four parameters are examined in order. In this specific case, all the BPDUs sent by DSW2 have the same Root Bridge ID, the same path cost to the Root and the same Sending Bridge ID. The only parameter left to select the best one is the Sending Port ID (Port ID = port priority + port index). And the port index of Gi1/2 is lower than the port index of Gi1/3 so the link between two Gi1/2 interfaces has been chosen as the primary link.
Therefore we must change the port priority to change the primary link. The lower numerical value of port priority, the higher priority that port has. In other words, we must change the port-priority on Gi1/3 of DSW2 (not on Gi1/3 of DSW1) to a lower value than that of Gi1/2 (the default port-priority value is 128).
Question 18
In a three-tier hierarchical campus network design, which action is a design best-practice for the core layer?
A. provide QoS prioritization services such as marking, queueing, and classification for critical network traffic B. provide advanced network security features such as 802. IX, DHCP snooping, VACLs, and port security C. provide redundant Layer 3 point-to-point links between the core devices for more predictable and faster convergence D. provide redundant aggregation for access layer devices and first-hop redundancy protocols such as VRRP
Answer: C
Explanation
The core should be highly available and redundant. The core aggregates the traffic from all the distribution layer devices, so it must be capable of forwarding large amounts of data quickly.
Considerations at the core layer include – Providing high-speed switching (i.e., fast transport) – Providing reliability and fault tolerance – Scaling by using faster, and not more, equipment – Avoiding CPU-intensive packet manipulation caused by security, inspection, quality of service (QoS) classification, or other processes
Reference: https://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=2202410&seqNum=4
Question 19
Which two network problems indicate a need to implement QoS in a campus network? (Choose two)
A. port flapping B. misrouted network packets C. excess jitter D. bandwidth-related packet loss E. duplicate IP addresses
Answer: C D
Question 20
In a Cisco SD-Access solution, what is the role of the Identity Services Engine?
A. It provides GUI management and abstraction via apps that share context. B. It is leveraged for dynamic endpoint to group mapping and policy definition. C. It is used to analyze endpoint to app flows and monitor fabric status. D. It manages the LISP EID database.
Answer: B
Explanation
DNA Controller – Enterprise SDN Controller (e.g. DNA Center) provides GUI management and abstraction via Apps that share context Identity Services – External ID System(s) (e.g. ISE) are leveraged for dynamic Endpoint to Group mapping and Policy definition Analytics Engine – External Data Collector(s) (e.g. NDP) are leveraged to analyze Endpoint to App flows and monitor fabric status
Question 21
A customer has completed the installation of a Wi-Fi 6 greenfield deployment at their new campus. They want to leverage Wi-Fi 6 enhanced speeds on the trusted employee WLAN. To configure the employee WLAN, which two Layer 2 security policies should be used? (Choose two)
A. WPA (AES) B. WPA2 (AES) + WEP C. 802.1X D. OPEN
Answer: C D
Explanation
Wi-Fi 6 (IEEE 802.11ax)
In greenfield we don’t need to use any security policy to reduce the wasting time of encryption/decryption.
Wi-Fi 6 does not support WPA with AES while WPA2 (AES) would slow down the connection -> Only 802.1X is the best choice left.
Question 22
Which outcome is achieved with this Python code?
client.connect (ip, port=22,username=usr,password=pswd)
stdin,stdout,stderr = client.exec_command('show ip bgp 192.168.10100 bestpath\n')
print(stdout)
A. displays the output of the show command in a formatted way B. connects to a Cisco device using SSH and exports the routing table information C. connects to a Cisco device using Telnet and exports the routing table information D. connects to a Cisco device using SSH and exports the BGP table for the prefix
Answer: D
Question 23
What is YANG used for?
A. scraping data via CLI B. providing a transport for network configuration data between client and server C. processing SNMP read-only polls D. describing data models
Answer: D
Explanation
YANG is used to model each protocol based on RFC 6020.
'보안 > 이론' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [CCNP] New ENCOR Questions Part 4 (0) | 2021.11.12 |
|---|---|
| [CCNP] New ENCOR Questions Part 5-2 (0) | 2021.11.12 |
| [CCNP] New ENCOR Questions Part 6 (0) | 2021.11.12 |
| [CCNP] New ENCOR Questions Part 7-4 (0) | 2021.11.12 |
| [CCNP] New ENCOR Questions Part 7-3 (0) | 2021.11.12 |
