Question 53
Refer to the exhibit. A network engineer troubleshoots an issue with the port channel between SW1 and SW2. Which command resolves the issue?

| *Aug 12 02:22:23.233: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Port-channel10, changed state to down *Aug 12 02:22:24.236: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Port-channel10,changed state to down *Aug 12 02:22:27.237: %ETC-5-L3DONTBNDL2: Gi0/1 suspended: LACP currently not enabled on the remote port *Aug 12 02:22:29.233: %ETC-5-L3DONTBNDL2: Gi0/0 suspended: LACP currently not enabled on the remote port |
A. SW1(config-if)#channel-group 10 mode active B. SW1(config-if)#channel-group 10 mode desirable C. SW2(config-if)#channel-group 10 mode on D. SW2(config-if)#switchport mode trunk
Answer: A
Question 54
Which new enhancement was implemented in Wi-Fi 6?
A. Wi-Fi Protected Access 3 B. 4096 Quadrature Amplitude Modulation Mode C. Uplink and Downlink Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access D. Channel bonding
Answer: C
Explanation
Wi-Fi 6 brings several crucial wireless enhancements for IT administrators when compared to Wi-Fi 5. The first significant change is using 2.4 GHz. Wi-Fi 5 was limited to only using 5 GHz. While 5 GHz is a ‘cleaner’ band of RF, it doesn’t penetrate walls and 2.4 GHz and requires more battery life. For Wi-Fi driven IoT devices, 2.4 GHz will likely continue to be the band of choice for the foreseeable future.
Another critical difference between the two standards is the use of Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) and MU-MIMO. Wi-Fi 5 was limited to downlink only on MU-MIMO, where Wi-Fi 6 includes downlink and uplink. OFDMA, as referenced above, is also only available in Wi-Fi 6.
Reference: https://www.extremenetworks.com/wifi6/what-is-80211ax/
Question 55
How is MSDP used to interconnect multiple PIM-SM domains?
A. MSDP depends on BGP or multiprotocol BGP for interdomain operation B. MSDP allows a rendezvous point to dynamically discover active sources outside of its domain C. MSDP SA request messages are used to request a list of active sources for a specific group D. MSDP messages are used to advertise active sources in a domain
Answer: D
Explanation
After a large PIM-SM network is divided into multiple PIM-SM domains, a mechanism is required to enable user hosts in a PIM-SM domain to receive multicast data from sources in another PIM-SM domain.
Multicast Source Discovery Protocol (MSDP) provides such a mechanism. It interconnects multiple PIM-SM domains to implement inter-domain multicast. RPs in PIM-SM domains set up MSDP peer relationships. By sending Source Active (SA) messages, the MSDP peers send the (S, G) information from the RP to which the source registers to the RPs in another PIM-SM domain.

Reference: https://support.huawei.com/enterprise/en/doc/EDOC1000027471?section=j009
Note: A benefit of using MSDP to interconnect multiple PIM-SM domains is to allow a rendezvous point (RP) to dynamically discover active sources outside of its domain but it is not “how”.
Question 56
Drag and drop the characteristics from the left onto the routing protocols they describe on the right.
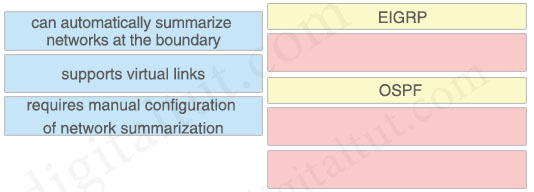
Answer:
EIGRP + can automatically summarize networks at the boundary
OSPF + supports virtual links + requires manual configuration of network summarization
Explanation
Unlike OSPF where we can summarize only on ABR or ASBR, in EIGRP we can summarize anywhere.
Manual summarization can be applied anywhere in EIGRP domain, on every router, on every interface via the ip summary-address eigrp as-number address mask [administrative-distance ] command (for example: ip summary-address eigrp 1 192.168.16.0 255.255.248.0). Summary route will exist in routing table as long as at least one more specific route will exist. If the last specific route will disappear, summary route also will fade out. The metric used by EIGRP manual summary route is the minimum metric of the specific routes.
Question 57
Drag and drop the characteristics from the left onto the protocols they apply to on the right.
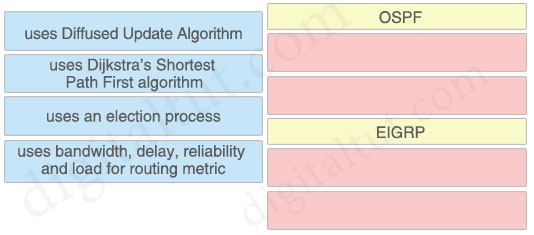
Answer:
OSPF + uses Dijkstra’s Shortest Path First algorithm + uses an election process
EIGRP + uses Diffused Update Algorithm + uses bandwidth, delay, reliability and load for routing metric
Question 58
How is 802.11 traffic handled in a fabric-enabled SSID?
A. converted by the AP into 802.3 and encapsulated into a VLAN B. centrally switched back to WLC where the user traffic is mapped to a VXLAN on the WLC C. centrally switched back to WLC where the user traffic is mapped to a VLAN on the WLC D. converted by the AP into 802.3 and encapsulated into VXLAN
Answer: D
Explanation
For a fabric-enabled SSID, the AP converts 802.11 traffic to 802.3 and encapsulates it into VXLAN, encoding the VNI and SGT information of the client.
Question 59
Drag and drop the wireless elements on the left to their definitions on the right.
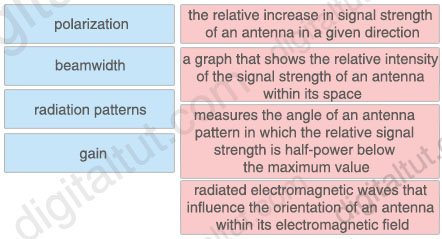
Answer:
+ the relative increase in signal strength of an antenna in a given direction: gain + a graph that shows the relative intensity of the signal strength of an antenna within its space: radiation patterns + measures the angle of an antenna pattern in which the relative signal strength is half-power below the maximum value: beamwidth + radiated electromagnetic waves that influence the orientation of an antenna within its electromagnetic field: polarization
Explanation
Beamwidth
The angle, in degrees, between the two half-power points (-3 dB) of an antenna beam, where more than 90% of the energy is radiated.
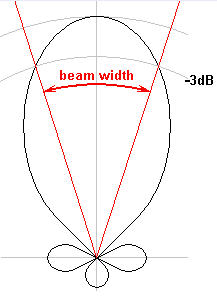
A radiation pattern defines the variation of the power radiated by an antenna as a function of the direction away from the antenna.
Polarization describes the way the electric field of the radio wave is oriented.
Antenna gain is the ability of the antenna to radiate more or less in any direction compared to a theoretical antenna.
Question 60
Refer to the exhibit.

R1
interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 10.1.1.10 255.255.255.0
ip nat inside
!
interface Serial0/0
ip address 209.165.201.1 255.255.255.224
ip nat outside
!
ip nat pool Busi 209.165.201.1 209.165.201.2 netmask 255.255.255.252
ip nat inside source list 1 pool Busi
!
access-list permit 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
!
R1#show ip nat statistics
Total active translations: 1 (0 static, 1 dynamic, 0 extended)
Outside Interfaces:
Inside Interfaces:
Ethernet0/0
Hits: 119 Misses: 1
Expired translations: 0
Dynamic mappings:
-- Inside Source
access-list 1 pool Busi refcount 1
pool fred: netmask 255.255.255.252
start 209.165.201.1 end 209.165.201.2
type generic, total addresses 2, allocated 1 (50%), misses 0
A network engineer configures NAT on R1 and enters the show command to verify the configuration. What does the output confirm?
A. R1 is configured with NAT overload parameters B. The first packet triggered NAT to add on entry to NAT table C. A Telnet from 160.1.1.1 to 10.1.1.10 has been initiated D. R1 to configured with PAT overload parameters
Answer: B
Question 61
Which congestion queuing method on Cisco IOS based routers uses four static queues?
A. low latency B. custom C. weighted fair D. Priority
Answer: D
Explanation
Priority Queuing (PQ): This type of queuing places traffic into one of four queues. Each queue has a different level of priority, and higher-priority queues must be emptied before packets are emptied from lower-priority queues. This behavior can “starve out” lower- priority traffic.
Question 62
What does the Cisco DNA REST response indicate?

A. Cisco DNA Center has the incorrect credentials for cat9000-1 B. Cisco DNA Center is unable to communicate with cat9000-1 C. Cisco DNA Center has the incorrect credentials for RouterASR-1 D. Cisco DNA Center has the incorrect credentials for cat3850-1
Answer: A
Explanation
From the output, we see the following facts from top to bottom: + ASR1001 is reachable + Cat9000 (C9300) has the incorrect credentials + Cat3850 is unreachable
Question 63
Which AP mode allows an engineer to scan configured channels for rogue access points?
A. local B. sniffer C. bridge D. monitor
Answer: D
Question 64
Where is radio resource management performed in a Cisco SD-access wireless solution?
A. control plane node B. DNA Center C. Cisco CMX D. wireless controller
Answer: D
Explanation
WLC is still responsible for: AP image/config, Radio Resource Management (RRM) and client session management and roaming.
Reference: https://www.ciscolive.com/c/dam/r/ciscolive/latam/docs/2018/pdf/BRKEWN-2020.pdf
Question 65
Refer to the exhibit.

Rapid PVST+ is enabled on all switches. Which command set must be configured on Switch1 to achieve the following results on port fa0/1? + When a device is connected, the port transitions immediately to a forwarding state + The interface should not send or receive BPDUs. + If a BPDU is received, it continues operating normally.
A. Switch1(config)# interface f0/1 Switch1(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast Switch1(config-if)# spanning-tree bpduguard enable
B. Switch1(config)# spanning-tree portfast bpduguard default Switch1(config)# interface f0/1 Switch1(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast
C. Switch1(config)#interface f0/1 Switch1(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast
D. Switch1(config)#spanning-tree portfast bpdufilter default Switch1(config)# interface f0/1 Switch1(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast
Answer: D
Explanation
BPDU Guard feature allows STP to shut an access port in the event of receiving a BPDU and put that port into err-disabled state so it is not the answer we want here.
BPDUFilter is designed to suppress the sending and receiving of BPDUs on an interface. If a BPDU is received on a Port Fast-enabled interface, the interface loses its Port Fast-operational status, and BPDU filtering is disabled -> BPDUFilter is the answer we want.
There are two ways to configure BPDU filtering feature, one in global configuration mode and one under a specific interface:
Configuring BPDU filter globally: Switch(config)#spanning-tree portfast bpdufilter default
Configure BPDU Filter on the interface: Switch(config-if)#spanning-tree bpdufilter enable (this overrides the global bpdufilter command above)
But the effect of these two commands are different and you should remember: + When BPDU filtering is enabled globally; and if BPDUs are seen, the port loses its PortFast status, BPDU filtering is disabled, the port returns to normal state + When BPDU filtering is enabled on a specific port, it prevents this port from sending or receiving BPDUs (so if BPDUs are seen, they will be dropped)
Question 66
Refer to the exhibit.

After running the code in the exhibit. Which step reduces the amount of data that NETCONF server returns to the NETCONF client, to only the interface’s configuration?
A. Create an XML filter as a string and pass it to get_config() method as an argument B. Use the txml library to parse the data returned by the NETCONF server for the interface’s configuration C. Create a JSON filter as a string and pass it to the get_config() method as an argument D. Use the JSON library to parse the data returned by the NETCONF server for the interface’s configuration
Answer: A
Explanation
Sometimes we are only interested in a very particular part of the config. NETCONF accomodates this with the ability to specify a filter. In below script, we will specify a filter that only shows the information for interface GigabitEthernet3. The get_config also accepts a filter parameter (documentation). So in below script, we will simply pass that filter to the get_config method and see what happens.

Reference: https://blog.wimwauters.com/networkprogrammability/2020-03-30-netconf_python_part1/
Question 67
A network engineer configures BGP between R1 and R2. Both routers use BGP peer group CORP and are set up to use MD5 authentication. This message is logged to the console of router R1:
| *Jun 5 33:34:33.033: %TCP-6-BADAUTH: Invalid MD5 digest from 10.10.10.1 (29832) to 10.120.10.1 (179) tableid -0 |
Which two configurations allow a peering session to form between R1 and R2? (Choose two)
A. R2(config-router)#neighbor 10.10.10.1 peer-group CORP R2(config-router)#neighbor CORP password Cisco
B. R2(config-router)#neighbor 10.10.10.1 peer-group CORP R2(Config-router)#neighbor PEER password Cisco
C. R1(config-router)#neighbor 10.10.10.1 peer-group CORP R1(config-router)#neighbor CORP password Cisco
D. R1(config-router)#neighbor 10.120.10.1 peer-group CORP R1(config-router)#neighbor CORP password Cisco
E. R2(config-router)#neighbor 10.120.10.1 peer-group CORP R2(config-router)#neighbor CORP password Cisco
Answer: C E
Explanation
The above message (“…Invalid MD5 digest from 10.10.10.1 (29832) to 10.120.10.1…”) was received on R1 so we can deduce the IP address of R1 is 10.120.10.1 and the IP address of R2 is 10.10.10.1. Therefore on R1 we have to configure “neighbor 10.10.10.1 …” while on R2 we have to use “neighbor 10.120.10.1 …”
Question 68
Which device makes the decision for a wireless client to roam?
A. wireless client B. access point C. wireless LAN controller D. WCS location server
Answer: A
Explanation
Roaming is a client side decision in 802.11 WiFi. Client devices listen for beacon frames or send probe requests to discover APs advertising the preferred SSID. The clients driver uses the received signal strength of beacons or probe responses to make decisions on whether to change APs or remain connected to the current AP.
Question 69
Refer to the exhibit.
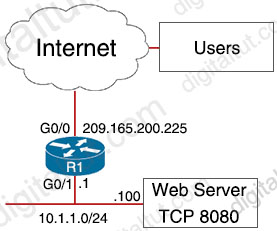
External users require HTTP connectivity to an internal company web server that is listening on TCP port 8080. Which command set accomplishes this requirement?
| Option A interface G0/0 ip address 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 ip nat inside |
Option B interface G0/0 ip address 209.165.200.225 255.256.255.224 ip nat inside interface G0/1 ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 ip nat outside ip nat inside source static tcp 209.165.200.225 80 10.1.1.100 8080 |
| Option C interface G0/0 ip address 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 ip nat inside interface G0/1 ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 ip nat outside ip nat inside source static tcp 10.1.1.1 8080 209.166.200.225 80 |
Option D interface G0/0 ip address 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 ip nat outside interface G0/1 ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 ip nat inside ip nat inside source static tcp 10.1.1.100 8080 interface G0/0 80 |
| Option E interface G0/0 ip address 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 ip nat outside interface G0/1 ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 ip nat inside ip nat inside source static tcp 209.165.200.225 8080 10.1.1.100 8080 |
A. Option A B. Option B C. Option C D. Option D E. Option E
Answer: D
Explanation
We need:
+ G0/0: NAT outside + G0/1: NAT inside -> Only Option D & Option E are correct
We need to configure local-ip before global-ip in the command ip nat inside source static local-ip global-ip so only Option D is correct.
Question 70
Which three elements determine Air Time efficiency? (Choose three)
A. evert-driven RRM B. data rate (modulation density) or QAM C. channel bandwidth D. number of spatial streams and spatial reuse E. RF group leader F. dynamic channel assignment
Answer: B C D
Explanation
Four things determine Air Time Efficiency 1. Data rate (Modulation density) orQAM -(how many Bit’s per Radio Symbol) 64 QAM is more robust but 1024 QAM is a lot faster 2. Number of spatial streams and spatial reuse (introduction of OFDMA and Resource Units) and UL/DL MU-MIMO 3. Channel bandwidth –How Many frequencies can we modulate at one time 4. Protocol overhead –Preamble/Ack/BA, Guard Interval “GI” etc.
Reference: https://www.ciscolive.com/c/dam/r/ciscolive/emea/docs/2020/pdf/BRKEWN-3010.pdf
Question 71
Which features does Cisco EDR use to provide threat detection and response protection?
A. containment, threat intelligence, and machine learning B. firewalling and intrusion prevention C. container-based agents D. cloud analysis and endpoint firewall controls
Answer: A
Explanation
In addition to continuous file analysis, it is important to note that an EDR is only as good at detecting files as the cyber threat intelligence that powers it. Cyber threat intelligence leverages large-scale data, machine learning capabilities, and advanced file analysis to help detect threats. The greater the cyber threat intelligence, the more likely it is your EDR solution will identify the threat. Without any cyber threat intelligence, an EDR solution is ineffective.
After detecting a malicious file, an EDR solution must be able to contain the threat. Malicious files aim to infect as many processes, applications, and users as possible. Segmentation can be a great defense within your data center to avoid lateral movement of advanced threats. Segmentation is helpful, but a proper EDR solution can help contain a malicious file before testing the edges of segmented areas of the network. Ransomware is a tremendous example of why you need to contain threats. Ransomware can be tricky to remove. Once it has encrypted information, your EDR needs to be able to fully contain ransomware to mitigate the damages.
Question 72
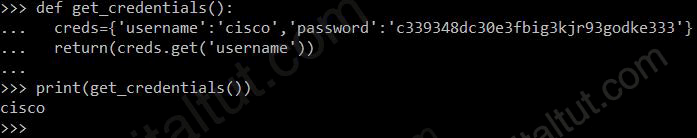
Refer to the exhibit.
def get_credentials():
creds={'username':'cisco','password':'c339348dc30e3fbig3kjr93godke333'}
return(creds.get('username'))
print(get_credentials())
What is the output of this code?
A. username: Cisco B. get_credentials C. username D. cisco
Answer: D
Explanation
“creds” is Dictionary type in Python so we can use the method “get” to get the value of an item.
Question 73
Which two threats does AMP4E have the ability to block? (Choose two)
A. DDoS B. ransomware C. SQL injection D. Microsoft Word macro attack E. email phishing
Answer: B D
Explanation
+ Advanced Malware Protection for Endpoints (AMP4E): provides malware protection on endpoints
Question 74
Refer to the exhibit.
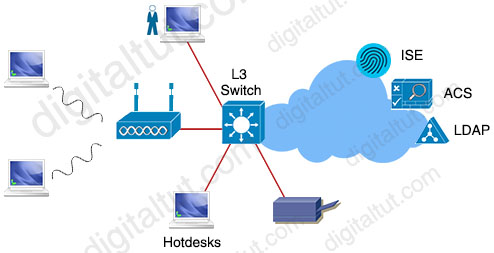
Which single security feature is recommended to provide Network Access Control in the enterprise?
A. 802.1X B. MAB C. WebAuth D. port security sticky MAC
Answer: A
Question 75
Refer to the exhibit.
%OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 10.0.0.2 on FastEthernet0/0 from FULL to DOWN,
Neighbor Down: Interface down or detached
%OSPF-6-AREACHG: 10.0.0.1/32 changed from area 0 to area 1
%OSPF-4-ERRRCV: Received invalid packet: mismatch area ID, from
backbone area must be virtual-link but not found from 10.0.0.2, FastEthernet0/0
What is the cause of the log messages?
A. OSPF area change B. hello packet mismatch C. MTU mismatch D. IP address mismatch
Answer: A
Question 76
What are two benefits of virtual switching when compared to hardware switching? (Choose two)
A. increased MTU size B. hardware independence C. VM-level isolation D. increased flexibility E. extended 802.1Q VLAN range
Answer: C D
Explanation
Virtual switches have benefits as well as virtual machines attached to them. They boost security by leveraging isolation, control and content inspection methods between virtual machines, which helps deter inter-switch link attacks. Moreover, with virtual switches, network administrators can control them with a hypervisor. Additionally, virtual switches can help with the migration of virtual machines across physical hosts by eliminating the need to reconfigure each virtual machine. They can also enhance operational efficiency, improve communications and scale system bandwidth capacity.
Reference: https://www.rcrwireless.com/20180328/fundamentals/physical-switches-vs-virtual-switches
Question 77
What are two characteristics of VXLAN? (Choose two)
A. It uses VTEPs to encapsulate and decapsulate frames. B. It has a 12-bit network identifier C. It extends Layer 2 and Layer 3 overlay networks over a Layer 2 underlay. D. It lacks support for host mobility E. It allows for up to 16 million VXLAN segments
Answer: A E
Explanation
VXLAN has a 24-bit VXLAN network identifier (VNI), which allows for up to 16 million (= 224) VXLAN segments to coexist within the same infrastructure. This surely solve the small number of traditional VLANs -> The first problem of VLAN has been resolved.
VTEPs connect between Overlay and Underlay network and they are responsible for encapsulating frame into VXLAN packets to send across IP network (Underlay) then decapsulating when the packets leaves the VXLAN tunnel.

VXLAN is a virtual overlay network which runs on the top of a physical underlay network. The underlay network may use any Layer 3 routing protocol like OSPF, EIGRP, IS-IS… to route packets so no Spanning Tree Protocol is required -> One of the major benefits of VXLAN technology is that it allows creating virtual Layer 2 segments over Layer 3 routed networks. Therefore answer C is not correct because “It extends Layer 2 and Layer 3 overlay networks over a Layer 3 underlay” (not Layer 2 underlay).
Question 78
Refer to the exhibit.
Router# traceroute 10.10.10.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Tracing the route to 10.10.10.1
1 10.0.0.1 5 msec 5 msec 5 msec
2 10.5.0.1 15 msec 17 msec 17 msec
3 10.10.10.1 * * *
An engineer is troubleshooting a connectivity issue and executes a traceoute. What does the result confirm?
A. The destination server reported it is too busy B. The probe timed out C. The destination port is unreachable D. The protocol is unreachable
Answer: B
Explanation
In Cisco routers, the codes for a traceroute command reply are:
! — success * — time out N — network unreachable H — host unreachable P — protocol unreachable A — admin denied Q — source quench received (congestion) ? — unknown (any other ICMP message)
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/ip-routed-protocols/22826-traceroute.html
Question 79
Refer to the exhibit.

A network engineer configures a new GRE tunnel and enters the show run command. What does the output verify?
A. The tunnel keepalive is configured incorrectly because they must match on both sites B. The tunnel destination will be known via the tunnel interface C. The tunnel will be established and work as expected D. The default MTU of the tunnel interface is 1500 byte.
Answer: B
Explanation
GRE keepalive packets may be sent from both sides of a tunnel or from just one side. If they are sent from both sides, the period and retry parameters can be different at each side of the link -> Answer A is not correct.
Tunnel interfaces by default will have 1476 bytes MTU. 24 bytes less the physical -> Answer D is not correct.
In this question, we turned on OSPF on all active interfaces (with the “network 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 area 0” command). So on SiteB the tunnel interface (192.168.100.2) is also running OSPF. When SiteA receives the OSPF advertisement from SiteB, it realizes it can reach the other side of the tunnel via OSPF (and it would not use the default route any more). In other words, it reaches the tunnel destination through the tunnel itself -> This causes “recursive routing” error.
Note: In order to avoid this error, do not advertise the tunnel destination IP address on the tunnel interface to other side.
Good recursive routing reference: https://networklessons.com/cisco/ccie-routing-switching/gre-tunnel-recursive-routing-error
Question 80
Refer to the exhibit.

An engineer has configured Cisco ISE to assign VLANs to clients based on their method of authentication, but this is not working as expected. Which action will resolve this issue?
A. require a DHCP address assignment B. utilize RADIUS profiling C. set a NAC state D. enable AAA override
Answer: D
Explanation
Dynamic VLAN assignment is one such feature that places a wireless user into a specific VLAN based on the credentials supplied by the user. This task of assigning users to a specific VLAN is handled by a RADIUS authentication server, such as Cisco ISE. This can be used, for example, to allow the wireless host to remain on the same VLAN as it moves within a campus network.
…
In order to accomplish dynamic VLAN assignment with WLCs based on ISE to AD group mapping, these steps must be performed: + ISE to AD integration and configuration of authentication and authorization policies for users on ISE + WLC configuration to support dot1x authentication and AAA override for correspondent SSID + End client supplicant configuration
Question 81
What is the function of a VTEP in VXLAN?
A. provide the routing underlay and overlay for VXLAN headers B. dynamically discover the location of end hosts in a VXLAN fabric C. encapsulate and de-encapsulate traffic into and out of the VXLAN fabric D. statically point to end host locations of the VXLAN fabric
Answer: C
===================== New Questions (added on 15th-Jun-2021) =====================
Question 82
If the noise floor is -90 dBm and the wireless client is receiving a signal of -75 dBm, what is the SNR?
A. -165 B. 83 C. 15 D. 1.2
Answer: C
Explanation
If your SNR measurements are already in decibel form, then you can subtract the noise quantity from the desired signal: SNR = S – N. This is because when you subtract logarithms, it is the equivalent of dividing normal numbers. Also, the difference in the numbers equals the SNR. In this question, SNR = -75 – (-90) = 15.
'보안 > 이론' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [CCNP] New ENCOR Questions Part 6 (0) | 2021.11.12 |
|---|---|
| [CCNP] New ENCOR Questions Part 7-4 (0) | 2021.11.12 |
| [CCNP] New ENCOR Questions Part 7-2 (0) | 2021.11.12 |
| [CCNP]New ENCOR Questions Part 7-1 (1) | 2021.11.12 |
| [CCNP]New ENCOR Questions Part 8 (0) | 2021.11.12 |
