Question 27
A network administrator has designed a network with two multilayer switches on the distribution layer, which act as default gateways for the end hosts. Which two technologies allow every end host in a VLAN to use both gateways? (Choose two)
A. HSRP B. GLBP C. MHSRP D. VRRP E. VSS
Answer: B C
Explanation
We can load share traffic in HSRP by using feature set called as Multiple HSRP wherein for a particular Group first path will be active and second as backup and for other group second path with be active and first the backup.
Question 28
Which measurement is used from a post wireless survey to depict the cell edge of the access points?
A. CCI B. Noise C. SNR D. RSSI
Answer: D
Explanation
The following are elements that you should consider when performing a post assessment of the environment.
Analyze and define the cell edge: This requires the use of AirMagnet Survey, although there are simple tools like Omnipeek or Wireshark that can be used to measure wireless traffic as a client roams from one AP to another. According to design best practices that revolve around the Cell Edge Design, a wireless handset should roam before the RSSI reaches -67 dBm. You can analyze signal strength and determine the approximate cell edge by measuring the signal strength in a beacon frame as you move from the center of one cell towards the edge of that cell.
Question 29
Refer to the exhibit.
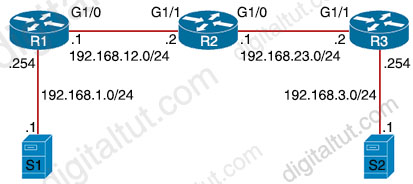
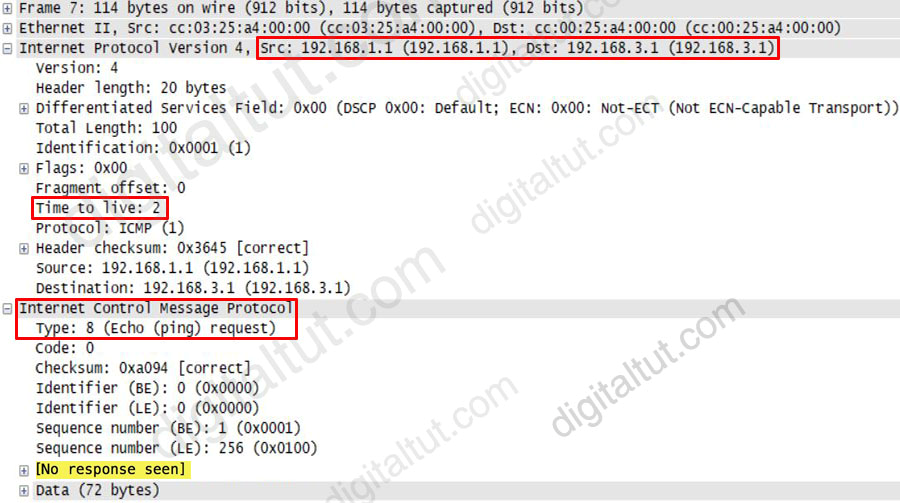
While troubleshooting a routing issue, an engineer issues a ping from S1 to S2. Which two actions from the initial value of the TTL? (Choose two)
A. The packet reaches R3, and the TTL expires B. R2 replies with a TTL exceeded message C. R1 replies with a TTL exceeded message D. The packet reaches R2 and the TTL expires E. R3 replies with a TTL exceeded message F. The packet reaches R1 and the TTL expires
Answer: B D
Explanation
“Routers decrement the TTL by 1 every time they forward a packet; if a router decrements the TTL to 0, it throws away the packet. This prevents packets from rotating forever.” We want to make it clear that before the router forwards a packet, the TTL is still remain the same.
For example in the topology below, pings to S0/1 and S0/0 of Router 2 have the same TTL.
If a router finds a TTL value of 1 or 0, it drops the datagram and sends an Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) time-to-live-exceeded message to the sender.
The picture below shows TTL values for each interface of each router and for Host B. Notice that Host A initializes ICMP packet with a TTL of 255:

Therefore in this question, if the initial TTL is 2, then R1 receives the packet with TTL of 2, then it decreases the TTL before forwarding to R2. R2 receives packet with TTL of 1 then decreases the TTL to 0 so R2 drops the packet ( -> Answer D is correct). R2 also replies back to the source with an ICMPv4 Type 11, Code 0 Time Exceeded message -> Answer B is correct.
Question 30
Refer to the exhibit.
Router#show access-list
Extended IP access list 100
10 permit ip 192.168.0.0 0.0.255.255 any
20 permit ip 172.16.0.0 0.0.15.255 any
Which command set must be added to permit and log all traffic that comes from 172.20.10.1 in interface GigabitEthernet0/1 without impacting the functionality of the access list?
| Option A Router(config)#ip access-list extended 100 Router(config-ext-nacl)#5 permit ip 172.20.10.0 0.0.0.255 any log Router(config)#interface GigabitEthernet0/1 Router(config-if)#access-group 100 in |
| Option B Router(config)#no access-list 100 permit ip 172.16.0.0 0.0.15.255 any Router(config)#access-list 100 permit ip 172.16.0.0 0.0.15.255 any log Router(config)#interface Gigabit Ether net0/1 Router(config-if)#access-group 100 in |
| Option C Router(config)#access-list 100 permit ip host 172.20.10.1 any log Router(config)#interface GigabitEthernet0/1 Router(config-if)#access-group 100 in |
| Option D Router(config)#access-list 100 seq 5 permit ip host 172.20.10.1 any log Router(config)#interface GigabitEthernet0/1 Router(config-if)#access-group 100 in |
A. Option A B. Option B C. Option C D. Option D
Answer: C
Explanation
Option A logs the whole subnet 172.20.10.0/24, not only host 172.20.10.1 so it is not correct. Option B does not log traffic coming from 172.20.10.1 so it is not correct.
We tested option D but the command “access-list 100 seq 5 permit ip host 172.20.10.1 any log” is not accepted as shown below:
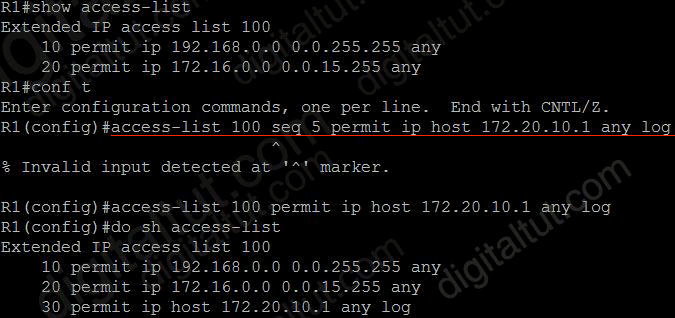
Option C would append the access-list (statement 30 in the above figure) so it is the best answer.
Question 31
What is the function of a fabric border node in a Cisco SD-Access environment?
A. To connect the Cisco SD-Access fabric to another fabric or external Layer 3 networks B. To collect traffic flow information toward external networks C. To attach and register clients to the fabric D. To handle an ordered list of IP addresses and locations for endpoints in the fabric.
Answer: A
Explanation
There are five basic device roles in the fabric overlay: + Control plane node: This node contains the settings, protocols, and mapping tables to provide the endpoint-to-location (EID-to-RLOC) mapping system for the fabric overlay. + Fabric border node: This fabric device (for example, core layer device) connects external Layer 3 networks to the SDA fabric. + Fabric edge node: This fabric device (for example, access or distribution layer device) connects wired endpoints to the SDA fabric. + Fabric WLAN controller (WLC): This fabric device connects APs and wireless endpoints to the SDA fabric. + Intermediate nodes: These are intermediate routers or extended switches that do not provide any sort of SD-Access fabric role other than underlay services.

Reference: CCNP and CCIE Enterprise Core ENCOR 350-401 Official Cert Guide
Question 32
How are the different versions of IGMP compatible?
A. IGMPv2 is compatible only with IGMPv1 B. IGMPv2 is compatible only with IGMPv2 C. IGMPv3 is compatible only with IGMPv3 D. IGMPv3 is compatible only with IGMPv1
Answer: A
Explanation
IGMPv3 is backward compatible with previous versions of the IGMP protocol. In order to remain backward compatible with older IGMP systems, IGMPv3 multicast routers MUST also implement versions 1 and 2 of the protocol.
Reference: https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc3376
IGMPv2 is only compatible with IGMPv1
Note: When saying “compatible”, we only mention about older version, not newer version. For example, we cannot say “IGMPv2 is compatible with IGMPv3” because IGMPv3 is newer. But we can say “IGMPv3 is compatible with IGMPv2”.
Question 33
What is one benefit of implementing a VSS architecture?
A. It provides multiple points of management for redundancy and improved support. B. It provides a single point of management for improved efficiency C. It uses GLBP to balance traffic between gateways D. It uses a single database to manage configuration for multiple switches
Answer: B
Explanation
VSS increases operational efficiency by reducing switch management overhead and simplifying the network. It provides a single point of management, IP address, and routing instance.
VSS can be managed with single management point from which you configure and manage the VSS. Neighbors see the VSS as a single Layer 2 switching or Layer 3 routing node, thus reducing the control protocol traffic. VSS provides a single VLAN gateway IP address, removing the need for the first-hop redundancy protocol (HSRP, VRRP, GLBP). Multichannel EtherChannel (MEC) allows you to bundle links to two physical switches in VSS, creating a loop-free redundant topology without the need for STP.
Reference: Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks (SWITCH) Foundation Learning Guide Book
Question 34
Which entity is a Type 1 hypervisor?
A. Oracle VM VirtualBox B. VMware server C. Citrix XenServer D. Microsoft Virtual PC
Answer: C
Explanation
Type 1 hypervisor has direct access to the hardware resources. Therefore they are more efficient than hosted architectures. Some examples of type 1 hypervisor are VMware vSphere/ESXi, Oracle VM Server, KVM and Microsoft Hyper-V. Xen/Citrix XenServer is also a type 1 hypervisor.
Question 35
An engineer runs the code against an API of Cisco DNA Center, and the platform returns this output.

What does the response indicate?
A. The authentication credentials are incorrect B. The URI string is incorrect C. The Cisco DNA Center API port is incorrect D. The HTTP method is incorrect
Answer: D
Explanation
From the output, we learn that a “Response [405]” was returned. The 405 Method Not Allowed is an HTTP response status code indicating that the specified request HTTP method was received and recognized by the server, but the server has rejected that particular method for the requested resource. Therefore answer B is not correct.
From this page (https://developer.cisco.com/docs/dna-center/#!command-runner/endpoints-and-methods-used), we may find out where the issue is:
“The Authentication endpoint used in this guide is /dna/system/api/v1/auth/token, which is valid for version 1.2.6 and above. The HTTP method used for the endpoint is POST and it requires for the user to send its credentials using Basic Authentication. Note: For systems with versions below that, the endpoint is /api/system/v1/auth/token”
Therefore the most suitable reason for this issue is we have to use “POST” instead of “GET” (in requests.get) -> Answer D is the best choice.
Question 36
What is a consideration when designing a Cisco SD-Access underlay network?
A. End user subnets and endpoints are part of the underlay network B. The underlay switches provide endpoint physical connectivity for users C. Static routing is a requirement D. It must support IPv4 and IPv6 underlay networks
Answer: B
Explanation
In SD-Access, the underlay switches (edge nodes) support the physical connectivity for users and endpoints. However, end-user subnets and endpoints are not part of the underlay network—they are part of the automated overlay network.
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/solutions/CVD/Campus/cisco-sda-design-guide.html
Question 37
What is a characteristic of a virtual machine?
A. It relies on hypervisors to allocate computing resources for it B. It is deployable without a hypervisor to host it C. It must run the same operating system as its host D. It must be aware of other virtual machines, in order to allocate physical resources for them
Answer: A
Question 38
What is one difference between Saltstack and Ansible?
A. SaltStack uses an API proxy agent to program Cisco boxes on agent mode, whereas Ansible uses a Telnet connection B. SaltStack uses the Ansible agent on the box, whereas Ansible uses a Telnet server on the box C. SaltStack is constructed with minion, whereas Ansible is constructed with YAML D. SaltStack uses SSH to interact with Cisco devices, whereas Ansible uses an event bus
Answer: A
Explanation
– Saltstack uses YAML (Python) same as Ansible. – Saltstack uses the push model for executing commands via the SSH protocol
Note: In SaltStack architecture, there is a core component called Salt-minion, which is a system that is being controlled by a Salt master. But that does not mean SaltStack is constructed with minion.
Question 39
What is the centralized control policy in a Cisco SD-WAN deployment?
A. list of ordered statements that define user access policies B. list of enabled services for all nodes within the cloud C. set of rules that governs nodes authentication within the cloud D. set of statements that defines how routing is performed
Answer: D
Explanation
In Cisco SD-WAN, there are two types of Centralized Control Policies that fulfill different objectives: + Topology – Topology policies control the route information such as omp, tloc, and service routes that are being redistributed to a list of sites. As the name implies, they are typically used for limiting the number of overlay tunnels between sites and controlling the overlay topology. + VPN Membership – VPN Membership policies are used to control the distribution of routing information for specific VPNs to a list of sites. A typical use-case is for creating guest networks that have Internet access but site-to-site communication is restricted.
Reference: https://www.networkacademy.io/ccie-enterprise/sdwan/what-is-a-centralized-control-policy
Question 40
Which command set configures RSPAN to capture outgoing traffic from VLAN 3 on interface GigabitEthernet 0/3 while ignoring other VLAN traffic on the same interface?
| Option A monitor session 2 source interface gigabitethernet0/3 rx monitor session 2 filter vlan 3 |
| Option B monitor session 2 source interface gigabitethernet0/3 tx monitor session 2 filter vlan 3 |
| Option C monitor session 2 source interface gigabitethernet0/3 rx monitor session 2 fitter vlan 1-2,4 – 4094 |
| Option D monitor session 2 source interface gigabitethernet0/3 tx monitor session 2 filter vlan 1-2, 4 – 4094 |
A. Option A B. Option B C. Option C D. Option D
Answer: B
Explanation
To “capture outgoing traffic” we have to use “tx” (transmitted) keyword. To only monitor VLAN 3 we have to use “monitor session 2 filter vlan 3”.
Question 41
Refer to the exhibit.
R1#show crypto isakmp sa
IPv4 Crypto ISAKMP SA
dst src state conn-id status
209.165.201.6 209.165.201.1 QM_IDLE 101 ACTIVE
After configurating an IPsec VPN, an engineer enters the show command to verify the ISAKMP SA status. What does the status show?
A. Peers have exchanged keys, but ISAKMP SA remains unauthenticated. B. ISAKMP SA is authenticated and can be used for Quick Mode. C. VPN peers agreed on parameters for the ISAKMP SA D. ISAKMP SA has been created, but it has not continued to form.
Answer: B
Explanation
The “show crypto isakmp sa” command displays all current Internet Key Exchange (IKE) security associations (SAs) at a peer.
QM_IDLE state means this tunnel is UP and the IKE SA key exchange was successful (authenticated), but is idle and may be used for subsequent quick mode exchanges. It is in a quiescent state (QM)
Question 42
Refer to the exhibit.

An engineer attempts to create a configuration to allow the Blue VRF to leak into the global routing table, but the configuration does not function as expected. Which action resolves this issue?
A. Change the access-list number in the route map B. Change the source network that is specified in access-list 101 C. Change the route-map configuration to VRF_BLUE D. Change the access-list destination mask to a wildcard
Answer: D
Explanation
We have to change the “10.10.1.0 255.255.255.0” to “10.10.1.0 0.0.0.255” in the ACL statement.
Question 43
Refer to the exhibit.

POSTMAN is showing an attempt to retrieve network device information from Cisco DNA Center API. What is the issue?
A. The token has expired B. The URI string is incorrect C. Authentication has failed D. The JSON payload contains the incorrect UUID
Answer: B
Explanation
We tested with Postman successfully with URI https://sandboxdnac.cisco.com/dna/intent/api/v1/network-device

But when changing URI to https://sandboxdnac.cisco.com/dna/intent/api/v1/network-devices (appending the last letter “s” in “network-devices”) we could reproduce the error in this question:
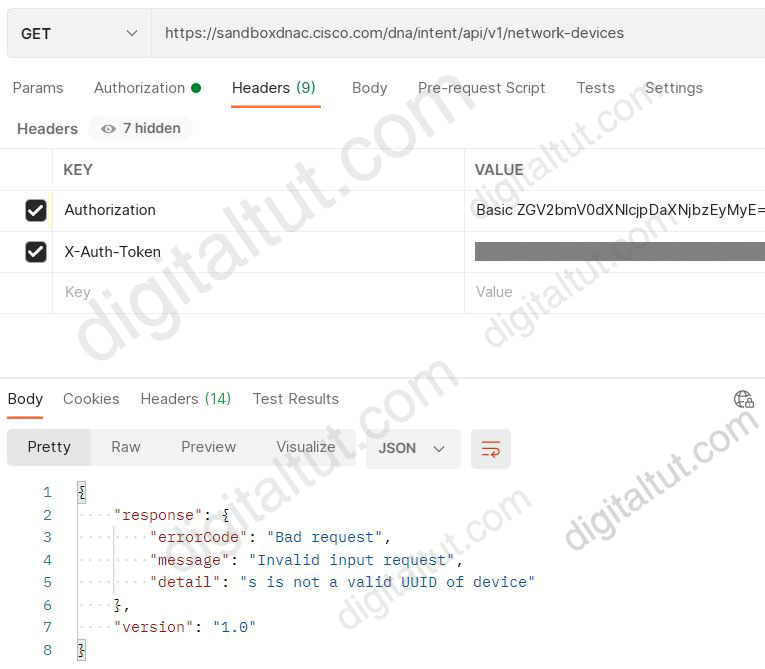
Therefore we can conclude the incorrect URI is the cause of this error.
If you want to check by yourself, this is a good tutorial for your reference https://garzum.net/cisco-dna-center-rest-api-calls-with-postman/
Question 44
Running the script causes the output in the exhibit. Which change to the first line of the script resolves the error?
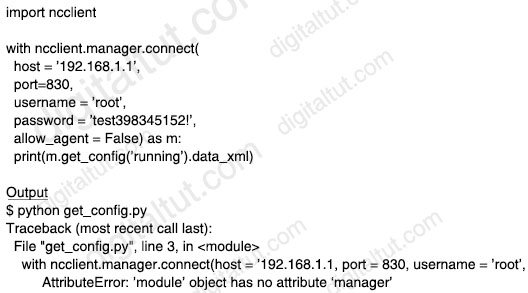
A. from ncclient import * B. import manager C. from ncclient import D. import ncclient manager
Answer: A
Explanation
Importing a module (“ncclient” in this case) does not automatically import submodules/functions (“manager” in this case) so the above script causes error.
Answer B is not correct as we cannot directly import “manager” as it is a function in “ncclient”.
Answer C is not correct as we did not specify anything after keyword “import”.
Answer D is not correct as it is missing a dot “.” (it should be “import ncclient.manager).
We tested both answer ‘from ncclient import *’ and answer ‘import ncclient.manager’ in Python and both of them worked well.
Question 45
An engineer configures HSRP group 37. The configuration does not modify the default virtual MAC address. Which virtual MAC address does the group use?
A. 00:00:0c:07:ac:25 B. 00:00:0c:07:ac:37 C. C0:39:83:25:258:5 D. C0.00:00:25:00:00
Answer: A
Explanation
The last two-digit hex value in the MAC address presents the HSRP group number. In this case 37 in decimal is 25 in hexadecimal -> Answer A is correct.
Question 46
Which Cisco DNA center application is responsible for group-based access control permissions?
A. Design B. Provision C. Assurance D. Policy
Answer: D
Question 47
Refer to the exhibit.

An engineer attempts to configure a trunk between switch SW1 and switch SW2 using DTP, but the trunk does not form. Which command should the engineer apply to switch SW2 to resolve this issue?
A. switchport mode access B. switchport nonegotiate C. no switchport D. switchport mode dynamic desirable
Answer: D
Question 48
Refer to the exhibit.
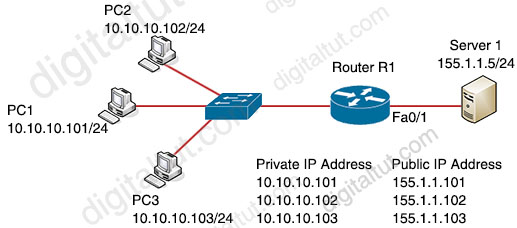
Which set of commands on router R1 allow deterministic translation of private hosts PC1, PC2, and PC3 to addresses in the public space?
| Option A RouterR1(config)#int f0/0 RouterR1(config)#ip nat inside RouterR1(config-if)#exit RouterR1(config)#int f0/1 RouterR1(config)#ip nat outside RouterR1(config-if)#exit RouterR1(config-if)#access-list 1 10.10.10.0 0.0.0.255 RouterR1(config)#ip nat pool POOL 155.1.1.101 155.1.1.103 netmask 255.255.255.0 RouterR1(config)#ip nat inside source list 1 pool POOL |
| Option B RouterR1(config)#int f0/0 RouterR1(config)#ip nat outside RouterR1(config-if)#exit RouterR1(config)#int f0/1 RouterR1(config)#ip nat inside RouterR1(config-if)#exit RouterR1(config)#ip nat inside source static 10.10.10.101 155.1.1.101 RouterR1(config)#ip nat inside source static 10.10.10.102 155.1.1.102 RouterR1(config)#ip nat inside source static 10.10.10.103 155.1.1.103 |
| Option C RouterR1(config)#int f0/0 RouterR1(config)#ip nat inside RouterR1(config-if)#exit RouterR1(config)#int f0/1 RouterR1(config)#ip nat outside RouterR1(config-if)#exit RouterR1(config)#ip nat inside source static 10.10.10.101 155.1.1.101 RouterR1(config)#ip nat inside source static 10.10.10.102 155.1.1.102 RouterR1(config)#ip nat inside source static 10.10.10.103 155.1.1.103 |
| Option D RouterR1(config)#int f0/0 RouterR1(config)#ip nat inside RouterR1(config-if)#exit RouterR1(config)#int f0/1 RouterR1(config)#ip nat outside RouterR1(config-if)#exit RouterR1(config-if)#access-list 1 10.10.10.0 0.0.0.255 RouterR1(config)#ip nat inside source list 1 interface f0/1 overload |
A. Option A B. Option B C. Option C D. Option D
Answer: C
Question 49
A client device roams between wireless LAN controllers that are mobility peers. Both controllers have dynamic interface on the same client VLAN. Which type of roam is described?
A. intra-VLAN B. intra-controller C. inter-controller D. inter-subnet
Answer: C
Explanation
Inter Controller-L2 Roaming: Inter-Controller (normally layer 2) roaming occurs when a client roam between two APs registered to two different controllers, where each controller has an interface in the client subnet.
Question 50
Which line must be added in the Python function to return the JSON object {“cat_9k”:”FXS193202SE”)?

A. return (json.dumps({d[‘hostname’]: d[‘serialNumber’] for d in json.loads(test_json)[‘response’]})) B. return (json.loads({for d in json.dumps(test_json)[‘response’]: d[‘hostname’]: d[‘serialNumber’]})) C. return (json.loads({d[‘hostname’]: d[‘serialNumber’] for d in json.dumps(test_json)[‘response’]})) D. return (json.dumps({for d in json.loads(test_json)[‘response’]: d[‘hostname’]: d[‘serialNumber’]}))
Answer: D
Explanation
We cannot have a for loop in a return statement so in fact all of the choices above are not correct but we still have to find the best answer.
The for loop must be put in front of d[‘hostname’]: d[‘serialNumber’] to start the loop -> Only answer B or answer D is correct.
Our first variable test_json is a string which we cannot loop through so we have to convert it into a dictionary type first with json.loads() function. Then we can use the for loop to iterate through the dictionary. The script below is an example:
import json
json_string = '{"key1": "value1", "key2": "value2"}'
#Load JSON string to a dictionary
json_dictionary = json.loads(json_string)
#Loop through dictionary keys
for key in json_dictionary:
print(key, ":", json_dictionary[key])
OUTPUT:
key1 : value1
key2 : value2
Therefore the correct syntax must be for d in json.loads(test_json)[‘response’]} -> Only answer D is correct.
We also tested it in Python and this is the result:
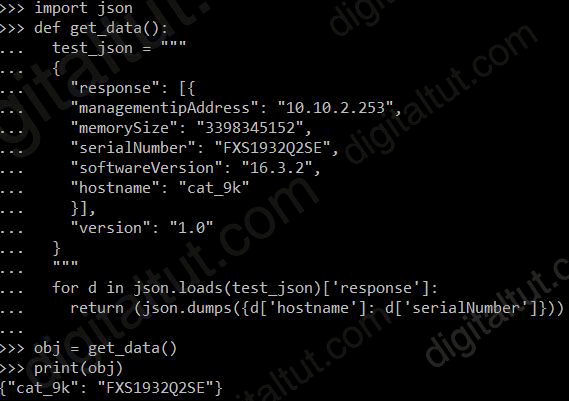
Note: + json.dumps() function converts a Python object into a json string. For example: json.dumps({‘name’: ‘John’,’age’: ’20’}) + json.loads() method parses a valid JSON string and convert it into a Python Dictionary.
Question 51
Which two operational models enable an AP to scan one or more wireless channels for rouge access points and at the same time provide wireless services to clients? (Choose two)
A. Sniffer B. Rouge detector C. Local D. FlexConnect E. Monitor
Answer: C D
Explanation
An LAP operates in one of six different modes: + Local mode (default mode): measures noise floor and interference, and scans for intrusion detection (IDS) events every 180 seconds on unused channels + FlexConnect, formerly known as Hybrid Remote Edge AP (H-REAP), mode: allows data traffic to be switched locally and not go back to the controller. The FlexConnect AP can perform standalone client authentication and switch VLAN traffic locally even when it’s disconnected to the WLC (Local Switched). FlexConnect AP can also tunnel (via CAPWAP) both user wireless data and control traffic to a centralized WLC (Central Switched). + Monitor mode: does not handle data traffic between clients and the infrastructure. It acts like a sensor for location-based services (LBS), rogue AP detection, and IDS + Rogue detector mode: monitor for rogue APs. It does not handle data at all. + Sniffer mode: run as a sniffer and captures and forwards all the packets on a particular channel to a remote machine where you can use protocol analysis tool (Wireshark, Airopeek, etc) to review the packets and diagnose issues. Strictly used for troubleshooting purposes. + Bridge mode: bridge together the WLAN and the wired infrastructure together. + Sensor mode: this is a special mode which is not listed in the books but you need to know. In this mode, the device can actually function much like a WLAN client would associating and identifying client connectivity issues within the network in real time without requiring an IT or technician to be on site.
Although Monitor and Rogue detector mode can detect rough APs but they do not handle data so they are not correct.
Rogue Detection A rogue is essentially any device that shares your spectrum, but is not in your control. This includes rogue Access Points, wireless router, rogue clients, and rogue ad-hoc networks. The Cisco UWN uses a number of methods to detect Wi-Fi-based rogue devices such as off-channel scanning and dedicated monitor mode capabilities. Cisco Spectrum Expert can also be used to identify rogue devices not based on the 802.11 protocol, such as Bluetooth bridges.
Off-Channel Scanning
This operation is performed by Local and Flex-Connect (in connected mode) mode APs and utilizes a time-slicing technique which allows client service and channel scanning with the usage of the same radio.
Question 52
Refer to the exhibit.

An engineer configures a new HSRP group. While reviewing the HSRP status, the engineer sees the logging message generated on R2. Which is the cause of the message?
A. A PC is on the network using the IP address 10.10.1.1 B. The HSRP configuration has caused a spanning-tree loop C. The HSRP configuration has caused a routing loop D. The same virtual IP address has been configured for two HSRP groups
Answer: D
Explanation
These messages specifically indicate that the router received a data packet that was sourced from the MAC addresses 0000.0c07.ac28, which is different from the MAC address of our HSRP group (0000.0c07.ac32). We also notice that 0000.0c07.ac28 is the virtual MAC address of another HSRP group (group 40 in particular; as 28 in hexadecimal equals to 40 in decimal).
Note: If the source MAC address of the error message is the same as our HSRP MAC address then the most likely cause is STP loop as our router received its own packet back.
'보안 > 이론' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [CCNP] New ENCOR Questions Part 7-4 (0) | 2021.11.12 |
|---|---|
| [CCNP] New ENCOR Questions Part 7-3 (0) | 2021.11.12 |
| [CCNP]New ENCOR Questions Part 7-1 (1) | 2021.11.12 |
| [CCNP]New ENCOR Questions Part 8 (0) | 2021.11.12 |
| 네트워크 기초 공부 자료 (0) | 2021.11.11 |
